Unmanned security systems
What are unmanned security systems?
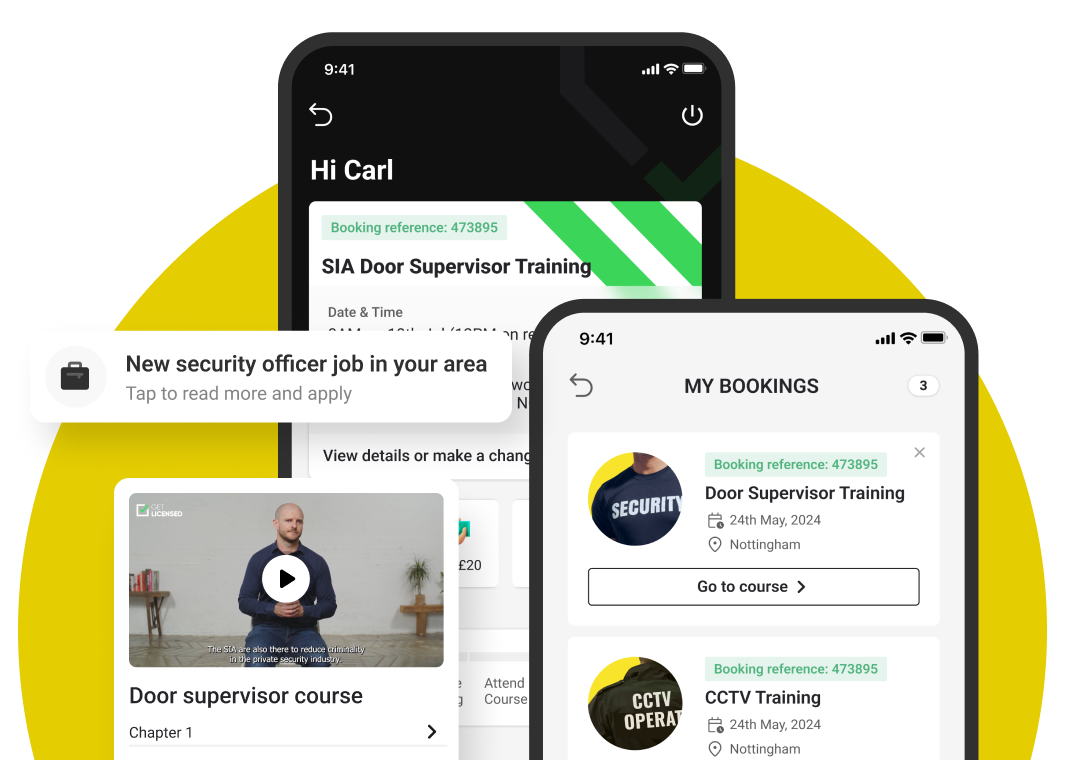
Unmanned security systems refer to autonomous or remotely operated technologies designed to enhance surveillance, detection, and response capabilities in various security contexts. These systems typically include drones, robotic ground vehicles, and static sensors equipped with cameras, thermal imaging, and other advanced detection equipment. Their primary purpose is to monitor environments, identify potential threats, and provide real-time data to human operators. These systems operate without direct human presence at the point of observation, relying instead on pre-programmed routes, artificial intelligence for anomaly detection, or remote control from a command centre. They are employed across diverse sectors, from protecting critical infrastructure and large commercial premises to border patrol and public event security, offering a persistent and often more discreet security presence.
Exploring the advantages of autonomous surveillance
Unmanned security systems offer a range of benefits that enhance overall security postures. These include continuous surveillance capabilities, often operating 24/7 without human fatigue, which significantly reduces the potential for oversight. Their deployment can also minimise risks to human personnel in hazardous or high-threat environments, allowing for remote monitoring and intervention. Furthermore, these systems can provide a cost-effective alternative to traditional manned guarding, particularly for large perimeters or remote locations. They offer scalability, allowing organisations to expand their security coverage as needed without a proportional increase in human resources. The data collected by unmanned systems, such as high-resolution imagery and sensor readings, can also be invaluable for forensic analysis and evidence gathering.
Integrating advanced technology into security operations
The integration of unmanned security systems into existing security frameworks requires careful planning and consideration. It is crucial to ensure that these systems complement, rather than replace, human security operatives, allowing for a more layered and robust defence. Effective integration involves establishing clear protocols for data collection, analysis, and response, ensuring that any alerts or anomalies are promptly addressed. Training for security personnel on how to operate, monitor, and maintain these advanced systems is also paramount. This ensures that the technology is utilised to its full potential and that human expertise remains central to the overall security strategy. Regular maintenance and software updates are essential to guarantee the continued reliability and effectiveness of unmanned security systems.

 Trustpilot
Trustpilot